Google Search Console is a tool provided by Google that helps users “improve the visibility of their content in search.”
The tool gives useful information about your website’s search visibility, including issues blocking Google from crawling and indexing your site, and allows you to request that Google index your pages.
In this article, we introduce 4 key features of Google Search Console that can help improve your website’s SEO. Let’s begin!
1. Performance: Check keywords that your website ranks for in Google
An effective SEO strategy is always data-driven. Without relevant data to measure your SEO success, you cannot truly improve your SEO.
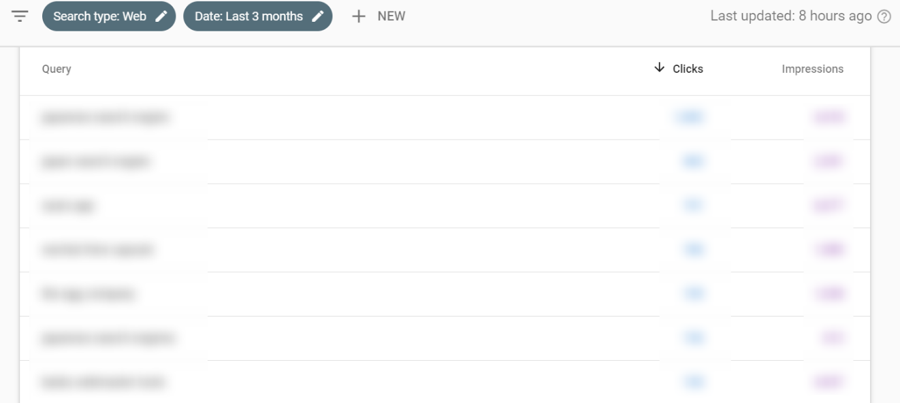
Google Search Console is useful in this area as it provides fundamental SEO data. You can find such data under Performance>Search results to see your website’s visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs).
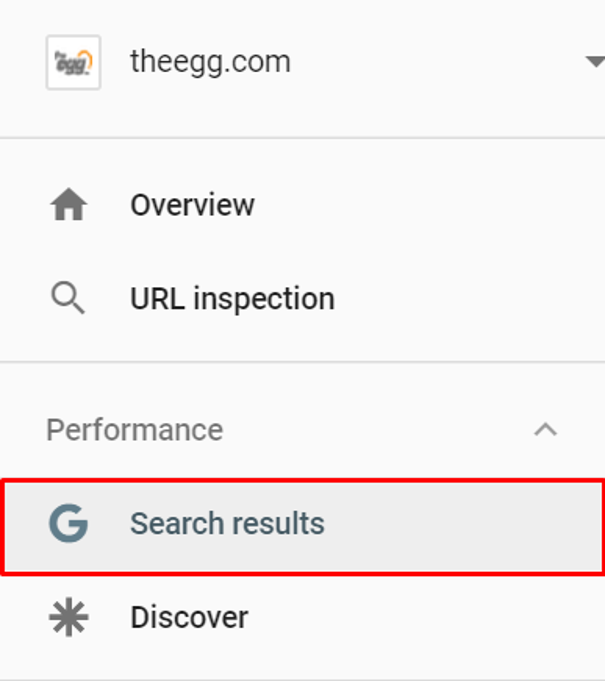
Another useful tab is Pages, which also shows the number of impressions and clicks but for each URL of your website. And most importantly, you can find out the keywords that your individual pages are ranking for.
Click on the URL that you want to investigate, then click the Queries tab again. This time, a page filter will be applied and only the keywords that the specified page is ranking for will be shown.
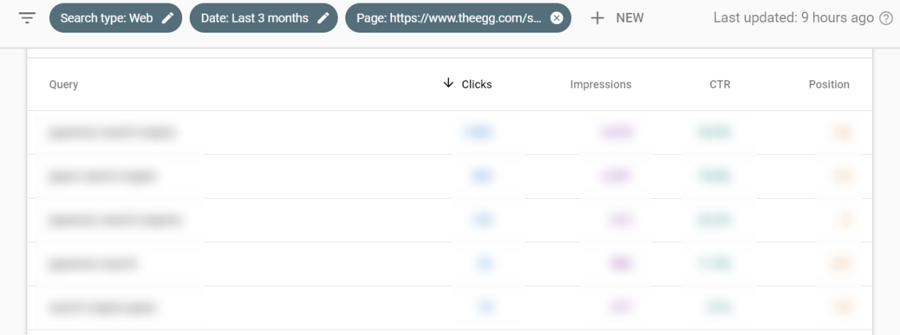
- Clicks and impressions: Discover which keywords effectively drive traffic.
- Click-through rate (CTR): Does a keyword that ranks high and has high search volume not generate a decent CTR? Filter out this keyword and optimize the title and description of the ranked page to improve the CTR.
- Position: You can check if your page ranks higher after optimization. You can also filter out keywords that are lower in ranking and diagnose what happened to your page or the SERP of the keywords.
The Performance report is a good start to measure and evaluate your SEO. It allows you to be creative and find out more about the organic visibility of your website.
2. Sitemaps: Submit your sitemap to Google
An XML sitemap is a list of webpages that you want Google to index. With a sitemap, Google can easily find and index all the key pages on your website.
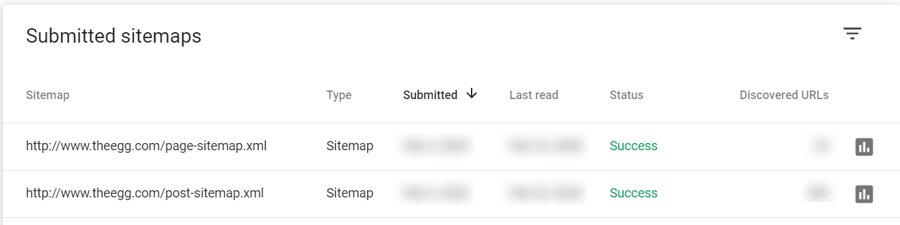
Once you have uploaded the sitemap to your domain, you can submit the sitemap to Google via Google Search Console under the Sitemaps tab.

3. Coverage: Find out how many pages of your website are indexed and what errors caused Google to not index your pages
It is always important to check if all the significant pages of your website are indexed properly—if they are not indexed by search engines, what’s the point of optimizing these pages?
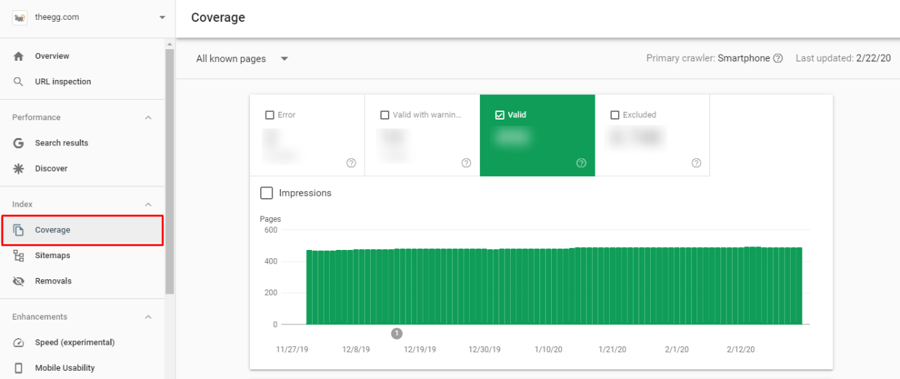
In Google Search Console, there is a handy tool called Coverage that allows you to check how many pages of your website are indexed and conversely the number of pages that aren’t indexed.
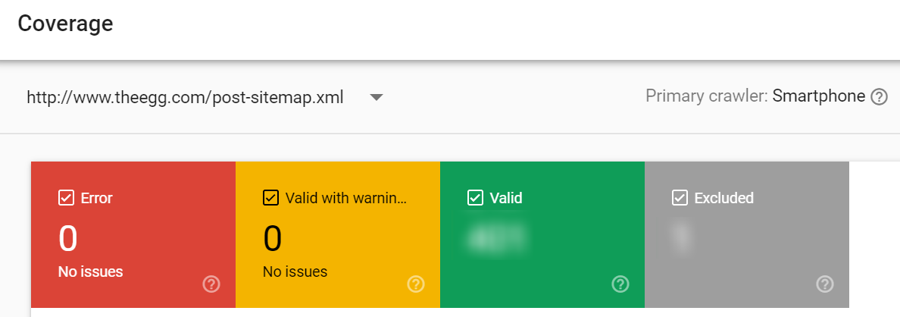
Click Coverage on the left and below is the dashboard that will be shown to you. The first thing you can look at is the Valid tab, which indicates the number of pages that are indexed by Google.
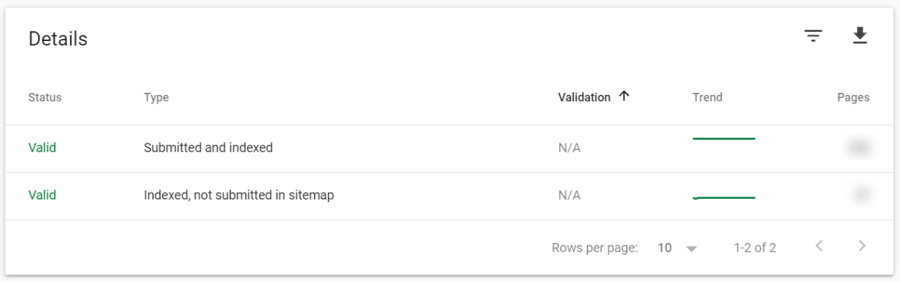
At the bottom, you can find more details about the indexed pages. It will show you how many pages are indexed as you have submitted to Google via an XML sitemap and the URL inspection tool (we’ll talk more about this later), and other pages that are indexed by Google.
Clicking on these tabs will bring you to the “examples” of your URLs that are indexed by Google. They are just examples as the table might not include all the pages that are indexed. If you are managing a large website, be reminded that the table row limit is 1,000 items so only a thousand of your pages will be listed.
By comparing the number of indexed pages and examples provided in the Valid tab, you can examine if all the URLs you have added in sitemap are indexed.
Moreover, you can check if there is a steady increase or sudden drop in the number of indexed pages. If you are constantly creating new content, the number of indexed pages should be gradually increasing. If these is a sudden drop, your website might have technical issues causing your pages to be deindexed.
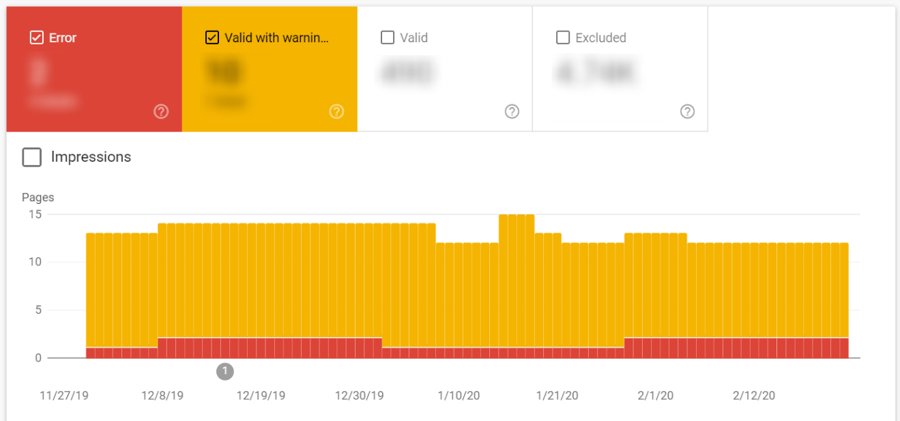
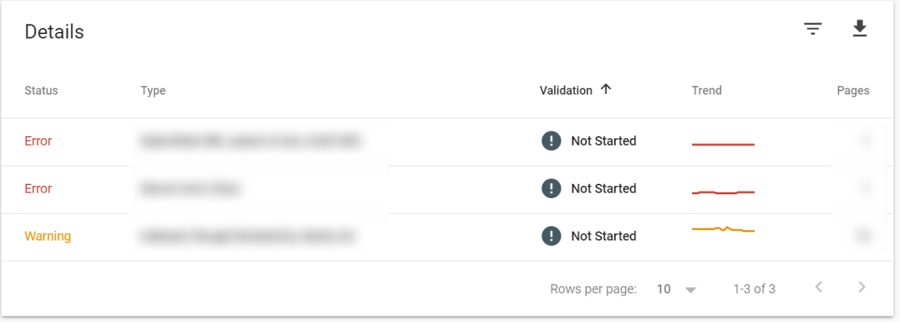
In addition to the Valid tab, there are 2 other tabs called Error and Valid with warnings. These show the number of pages that aren’t indexed but are instead having issues. Similarly, you can find the details of the issues at the bottom of the page.
After you have resolved the issue that is indicated in Google Search Console, you can click on the error in the Details section. Then use Validate Fix to ask Google to recrawl pages.
4. URL inspection: Request that Google (re)index and (re)crawl a page
The URL inspection tab in Google Search Console is a tool that you can use to ask Google to index (or reindex) a specific page on your website. The tool is especially useful when:
- An important page on your website is not indexed by Google
- You created a new page and Google has not yet discovered it
- You updated a page and want Google to recrawl it
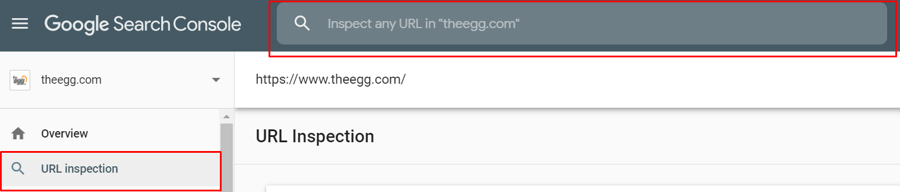
The tool is straightforward and easy to use. In Google Search Console, click URL inspection on the left and then enter the URL you want to submit into the search bar. It will take few minutes for Google to test the URL.
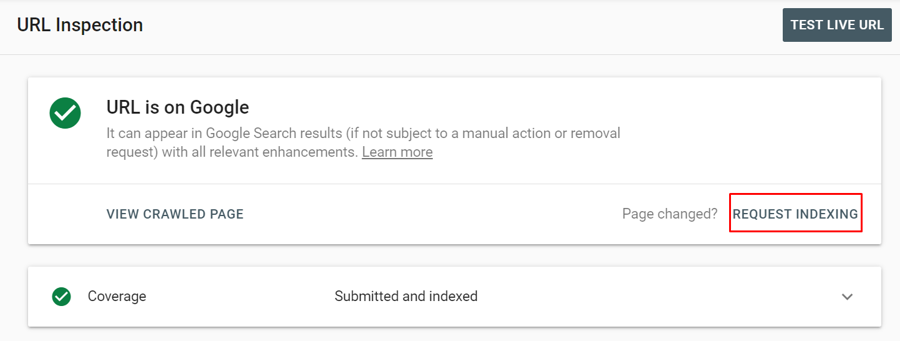
After the test, Google will show whether the URL has any significant indexing issues. If there are no issues, click Request Indexing to ask Google to index your page.
And it’s done! Google said their crawling can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks. But we have seen that most of time it will only take few days for Google to complete the request. You can check if the page gets indexed by entering the URL in the URL inspection tool.