How to Successfully Conduct Indexing SEO
The role of search engines is to discover, understand, and organize the internet’s content to deliver the most relevant results to a user’s search query. But have you wondered how search engines do that?
Answer? Indexation.
When you search for information on Google, for example, you are not searching from the entire internet but rather from Google’s index, or more simply, Google’s library of webpages. In short, only the pages that Google has indexed will appear on its organic search results pages.
To visualize this, here is a 3-step pipeline that most search engines use to deliver the most relevant results to users:
- Crawling: Search engines use web crawlers (bots or spiders) to scour the web and discover webpages. Pages that have already been discovered are crawled every so often to detect any changes to their content.
- Indexing: Search engines store and organize content discovered during crawling. Once indexed, pages will appear on search engine results pages (SERPs).
- Ranking: After indexation, search engines use ranking algorithms to analyze ranking factors like page speed, content relevancy, and page authority to determine a page’s ranking.
In this article, let’s dive deeper into why indexing SEO is important, how it works and how to get Google index your website so that you can maximize your SERP visibility and attract valuable traffic.
Why is indexing important?
Indexation is necessary for webpages to appear on SERPs—if not successfully indexed, your page cannot rank for relevant queries and, thus, will not attract organic traffic to your website.
Hence, if your site has any unresolved indexation issues, the work that went into creating and designing your website would go to waste.
Does Google index all my pages?
In short? No. This was verified by Google’s senior webmaster trends analyst, John Mueller, who stated that it is perfectly normal for at least 20% of a site not to get indexed:
“The other thing to keep in mind with regards to indexing, is it’s completely normal that we don’t index everything off of the website. So, if you look at any larger website or any even midsize or smaller website, you’ll see fluctuations in indexing. It’ll go up and down and it’s never going to be the case that we index 100% of everything that’s on a website.”
Google Search Central: John Mueller at the English Google SEO office-hours from August 13, 2021
However, this does not mean that since Google doesn’t index all of your pages, you can rest on your laurels. Instead, it is imperative that you consistently optimize your pages to help them get indexed and ranked, especially with competition mounting on the SERP.
How long does it take for Google to index a page?
Google generally takes anywhere between four days to four weeks to crawl and index a webpage, the speed of which is affected by the following site-related factors:
- Your website’s reliance on client-rendered JavaScript
- Your website’s content quality
- The size of your website (i.e., number of pages)
WANT DIGITAL INSIGHTS STRAIGHT TO YOUR INBOX?
HOW TO CHECK IF MY WEBSITE IS INDEXED BY GOOGLE
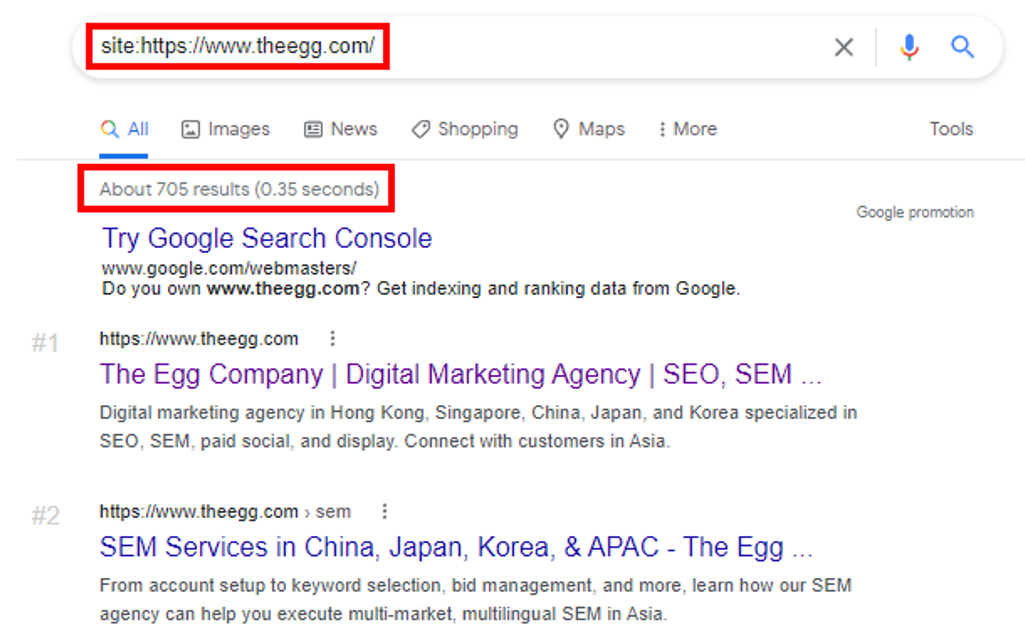
To check whether Google has indexed your website and how many pages are indexed, open Google and search for your site (e.g., “site: yourwebsite.com”). If your website is not indexed, no pages will appear when you conduct this search.
Google search your site (e.g., “site: https://www.theegg.com/”) to see how many pages are indexed
Alternatively, you can use the Page Indexing Report on Google Search Console for a more accurate reading of your website’s indexation status.
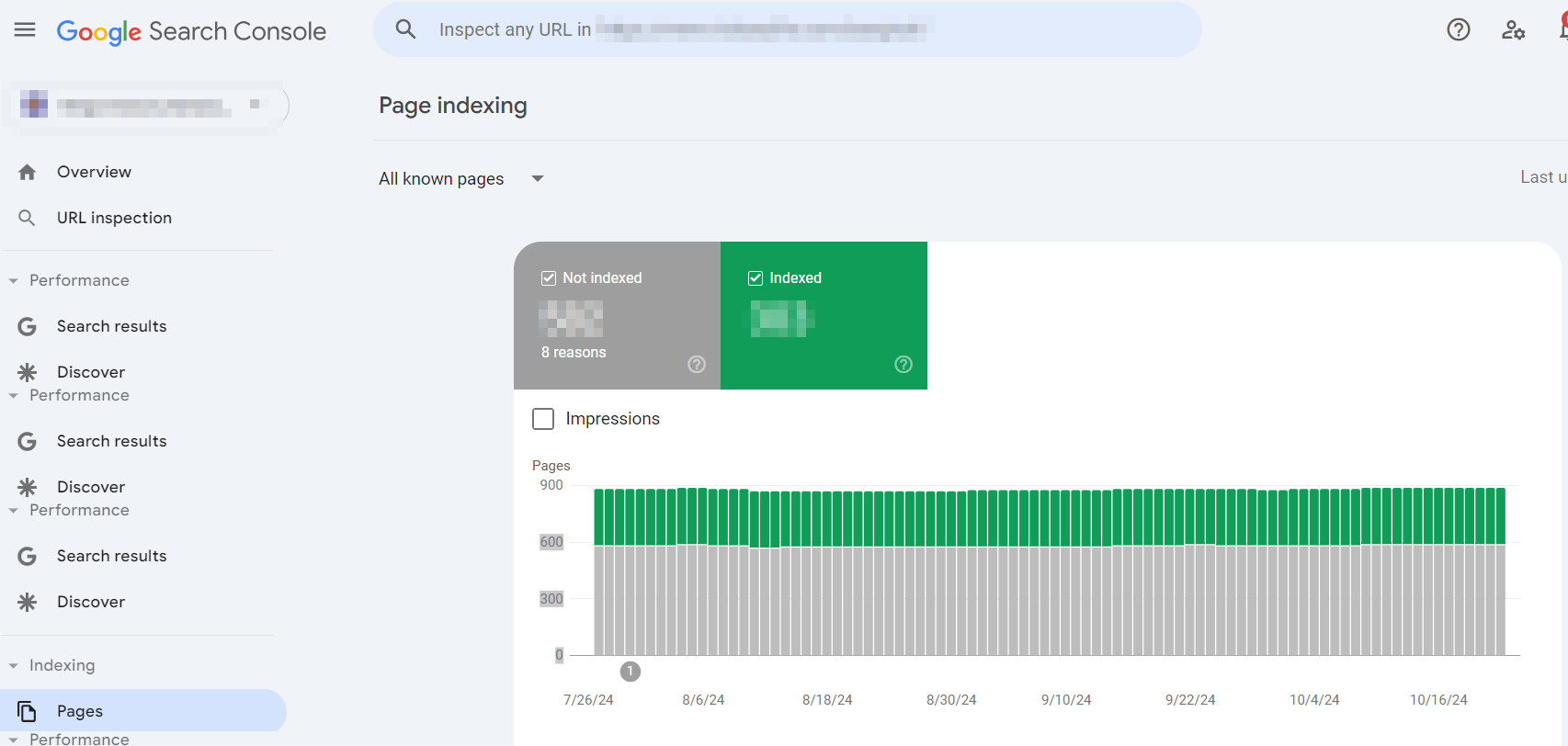
GSC’s Page Indexing Report categorizes pages as Indexed and Not Indexed:
- Indexed: These pages have been successfully indexed.
- Not indexed: These pages are not indexed due to a list of reasons.
So, if Google has not indexed a webpage that you would like indexed, there are three issues to resolve:
- Noindex meta tag
- Robots.txt file
- Canonical tags
Noindex meta tag
If you want a page to be indexed, then it should be void of noindex meta tags, which are inserted in a page’s source code to tell Google not to index it.
robots.txt file
Remove any disallow directives from your robots.txt since they tell search engines which URLs to avoid indexing.
Canonical tags
Canonical tags signal to Google the master copy of a page with duplicate versions—and it is the master copy that gets indexed.
Therefore, if you want to have your page indexed, it should have a self-referencing canonical tag and not one pointing to another page.
HOW TO get google to index my site
1. Use an XML sitemap
XML sitemaps serve as roadmaps of all the indexable pages on your website, thereby making it more efficient for search engines to crawl. They also help differentiate pages and files you want Google to index as a priority.
Here’s what Google defines as an XML sitemap:
“Search engines like Google read this file to crawl your site more efficiently. A sitemap tells Google which pages and files you think are important in your site, and also provides valuable information about these files. For example, when the page was last updated and any alternate language versions of the page.”
Google Search Central – Learn about sitemaps
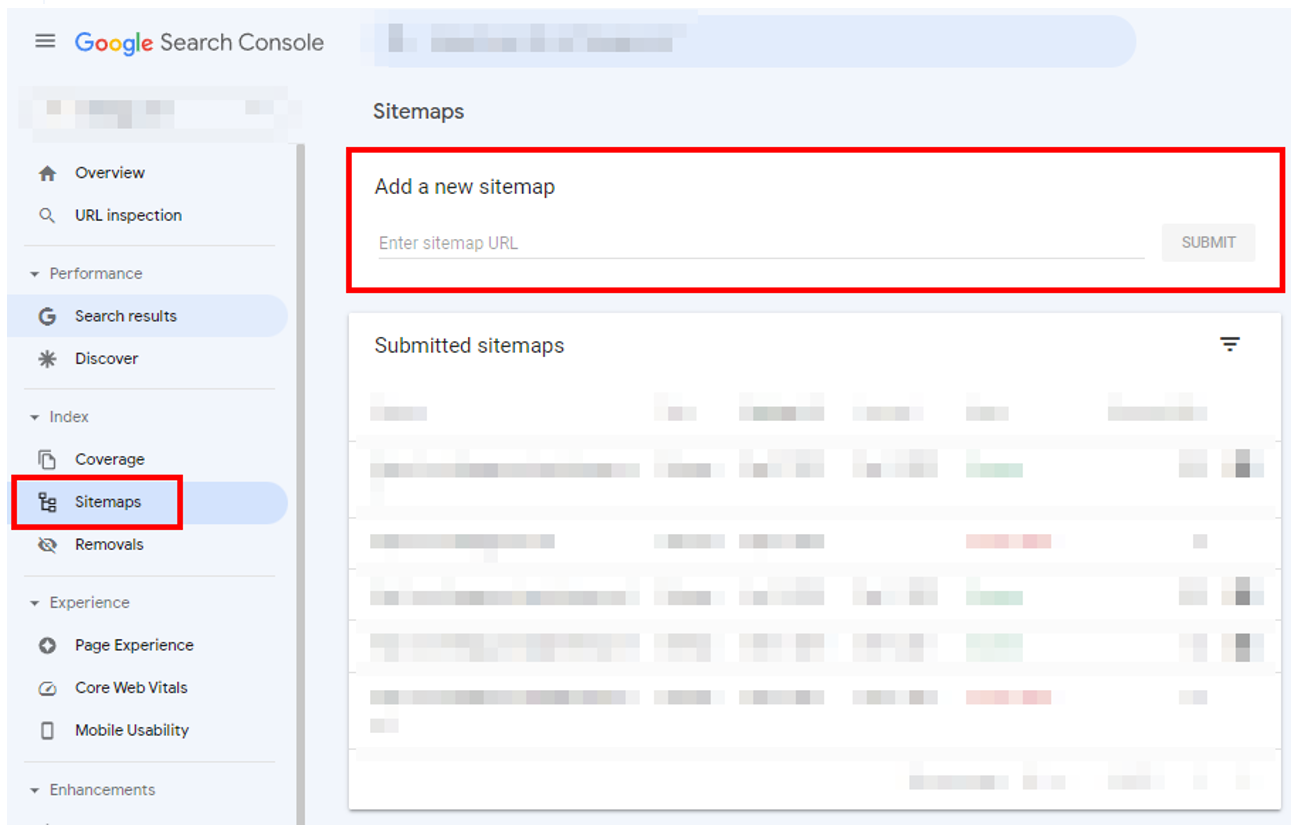
After creating an XML sitemap, you will need to submit it to Google Search Console’s Sitemap Tools.
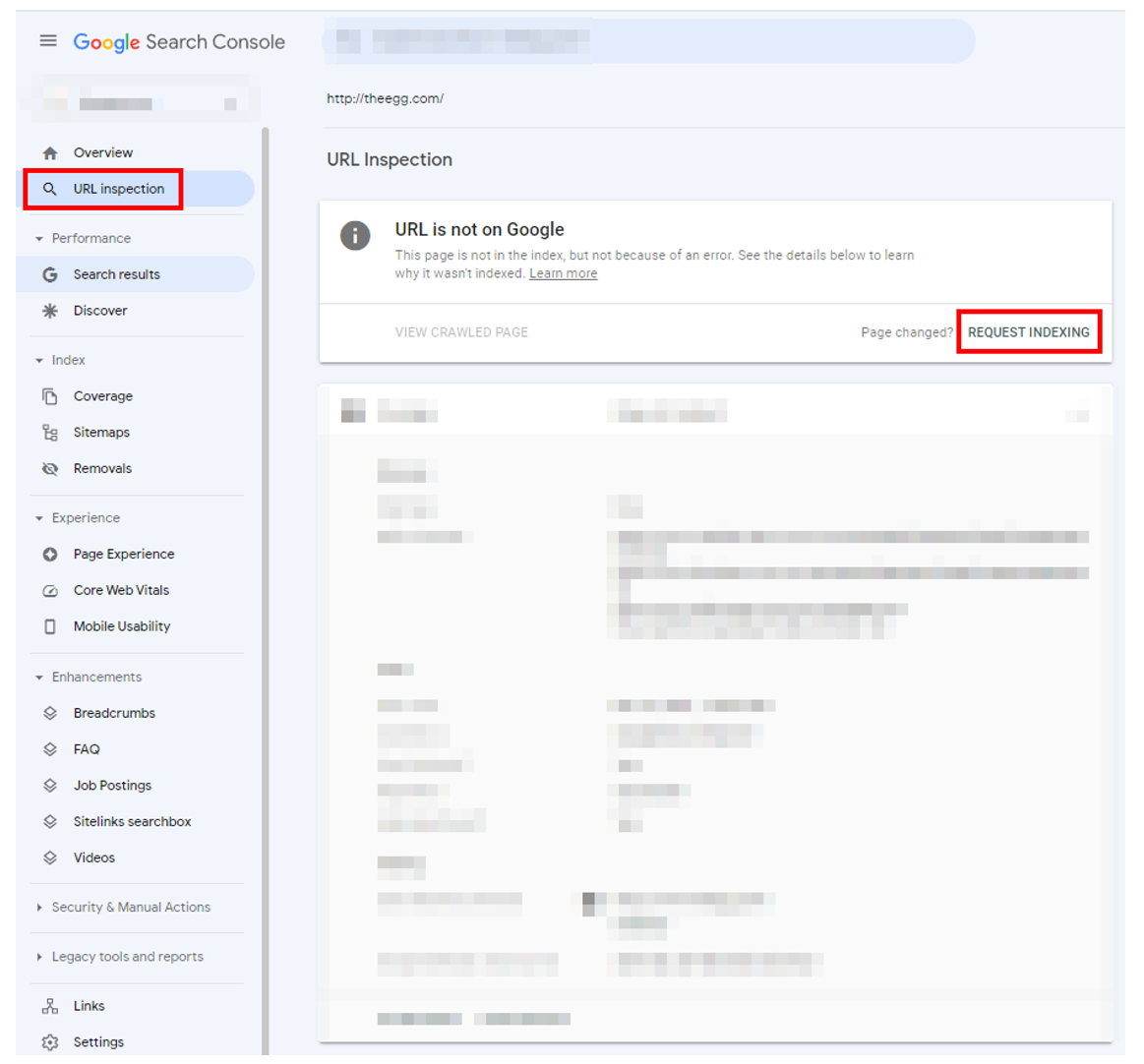
2. Use the GSC URL Inspection Tool
After publishing a new webpage or modifying content on existing ones, you should use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool to inform Google of these changes.
To inspect your page, click on Request Indexing in the URL Inspection Tool. Note, however, that if your page was just recently submitted, Google Search Console will show that the “URL is not on Google”.
The URL Inspection Tool is effective for getting Google to index your pages. Previously, Google could index pages within five minutes after requested. But now Google takes more time to index pages.
Also, note that there is a quota for URL submissions—requesting Google to index the same URL multiple times will not get it crawled any faster.
3. Internal Linking
Another SEO factor affecting your site’s indexation is internal linking. Based on our experience, it is common to find pages on XML sitemaps that aren’t linked from any other page within the same domain. We call these orphaned pages.
Although indexable, orphaned pages are difficult to locate by both users and search engines. Furthermore, orphaned pages do not have internal links pointing to them, resulting in lower page authority and a higher likelihood of Google deciding not to index these pages altogether.
For more information, check out this guide on how to find and resolve orphaned pages using Screaming Frog.
4. Carefully manage the robots.txt file and noindex tag
The robots.txt file and the noindex tag are essential in directing Google’s crawling and indexing activities on your website. The robots.txt file can instruct Google’s crawlers not to crawl specific pages on your site, while the noindex tag explicitly tells Google not to include a certain page in its index.
These tools are effective in preventing certain sections or pages of your website from being indexed. However, it’s important to apply them judiciously—only on pages you intentionally want to remain unindexed. Ensure that important pages are not restricted by the robots.txt file or mistakenly marked with the noindex tag, as this could hinder their visibility in search results.
5. avoid duplicate content
Large amounts of duplicate content can turn Google’s crawl budget into waste and hinder search engines from properly indexing your website. Ideally, pages should be unique and have content distinguishable from each other so that Google would index each one of them. However, when you have very similar, or even identical content appearing on multiple pages on your website, it confuses Google and makes it hard for the Search Engine to determine which version to index. As the identical pages compete against each other, it lowers the performance of all the pages.
Should your website contain a large amount of duplicate content, there are multiple ways to fix them. However, be cautious with the implementation. For instance, it’s important to avoid canonicalizing a page with a ‘noindex’ tag, as this will further compliate the indexing process.
6. create high-quality content
Creating high-quality content is not just about engaging your audience; it is also a crucial factor in getting Google to index your website more effectively. Google’s algorithms are designed to prioritize content that offers value, relevance, and uniqueness. By creating informative, well-researched, and original content, you signal to Google that your website is a valuable resource worth indexing. As a result, Google is more likely to index your website quickly and rank it higher in search results, making your site more visible to potential visitors.
7. build quality backlinks to your site
Building quality backlinks is a cornerstone strategy for an SEO strategy and can prompt Google to index your website quickly. Backlinks, especially those from reputable sites, serve as a signal of trustworthiness and indicate to Google that your content is valuable and worthy of being ranked and indexed. As these links pass authority to your webpage, it will get indexed by Google faster.
Moreover, much like internal linking, backlinks from other websites can accelerate the discovery process, as Google’s bots navigate through links to crawl new content. When a high-traffic and reputable website links to your site, it is likely that search engine crawlers will follow that link to your site, leading to the discovery of new content and pages that need to be indexed.
***
Remember that above all, your site must be indexed before it can rank on search engines. As such, the best place to start your indexation journey would be to consider these questions:
- Are the number of indexed pages on your site increasing or decreasing?
- Are the number of pages showing errors increasing or decreasing?
- Can Google easily find your pages?
- Are there any technical factors preventing Google from indexing your pages?
- Are the pages you want to get indexed (1) valuable and (2) intended to be indexed?
After answering these questions, you should be equipped to resolve your website’s indexation issues to provide better value and an optimized experience for your users.
This article has been updated by Helena Xiao in 2024.