SEO in Korea: History of the Naver Blog Search Algorithm
On the universal Naver SERP, there are myriad ad structures with between 4-10 text ads for any given search and even more ad sections below the fold.
In other words, Naver prioritizes paid search results.
Contrary to other search engines around the world (particularly Google), Naver has less space on its search engine results page (SERP) for purely organic listings from your website pages. Website organic results generally get pushed to the bottom or are sometimes not even visible at all.
That said, Naver’s organic search results appear in two forms: your website pages and Naver-specific properties, such as Café, Blog, Knowledge iN, Shopping, etc. These Naver properties make Naver SEO more intricate and complex than Google SEO even if just by their sheer variety alone.
Therefore, we recommend starting your Naver SEO journey by working with Naver properties first. In particular, you can start with Naver Blog (as that’s got the greatest number of monthly active users among Naver properties).
Since 2012, Naver has launched 4 different algorithms for its Blog search property (these algorithms have also been applied to Naver Post and Café).
In this article, learn the history of Naver’s Blog search algorithms along with insights for successful SEO in Korea today.
Naver Blog Search Algorithm: Libra (2012-2016)
What is the Naver Libra Algorithm and how does it work?
Back in the day, it was said that the only strategy to rank higher on Naver SERPs was to create as many content pieces as possible for Naver properties (e.g., Naver Café, Blog, Knowledge iN, Shopping, etc.).
Essentially, the more Naver property posts, the more comments, the more shares, the more engagement, the higher the rank. However, this got abused such that the Naver SERP became dominated with low-quality content.
What are the limitations of Libra?
With the Naver Libra algorithm, lots of black hat SEO strategies went viral. Advertisers and brands alike created multiple blogs with low-quality articles that included keyword stuffing tactics or even adverts to increase the ranking of their supposedly organic blog.
As such, commercial content—rather than user-focused, high-quality content—filled most of the Naver Blog search results at that time.
This was quite counterproductive because people search Naver Blog to find informative content and useful information. As such, Naver Blog was losing its credibility due to its increased number of advertisements and low-quality content.
Poor Uses of Naver Libra Algorithm
Blog content created with black hat tactics (as shown in the images below) used to account for the majority of Naver Blog search results. This included:
- Keyword stuffing
Black hat SEO example: Title stuffed with the same keyword (‘hydration facial cream’ used five times)
- Content filled with meaningless words
Black hat SEO example: Meaningless content (e.g., if strawberry milk was poured over, again instead outskirt and…)
- Content with hidden or small text that people could not easily decipher.
Black hat SEO example: Hidden content
To solve these problems, Naver introduced a new Blog search algorithm: C-Rank.
Naver Blog Search Algorithm: C-Rank (2016-present)
What is the Naver C-Rank Algorithm and how does it work?
The Naver C-Rank algorithm evaluates the credibility of the content creator, rather than the content itself (the ‘C’ in C-Rank stands for ‘creator’).
One of the critical factors of the Naver C-Rank algorithm in measuring credibility and popularity is how deeply a content creator delves into a specific topic (or interest of users).
It prioritizes content creators who are professional writers and subject matter experts on a single topic over a long period of time rather than uncredentialed bloggers writing on multiple categories.
What are the considerations of the Naver C-Rank algorithm?
According to Naver, the C-Rank algorithm considers the items below when ranking content on the SERP.
Blog Collection
This considers the quality of content based on essentials like title, body text, images, and links.
Naver Database
This considers the degree of credibility of content according to Naver’s database.
Search Log
This considers the popularity of the blog by calculating the search log data of users.
Chain Score
This considers the credibility and popularity of the blog with sources like Naver’s websites, webpages, and news section.
Blog Activity
This considers the recency and activity of the blog.
Blog Editor Topic Score
This considers how focused the blog is on a specific topic.
What are the limitations of the Naver C-Rank algorithm?
It’s obvious that this algorithm has a critical drawback: search engine results are determined based on the quality of where they come from rather than the quality of the content itself.
Chances are that professional writers can create quality content, but that doesn’t necessarily mean that a good blog always writes informative articles and that a less professional blog always creates low-quality articles.
As a result, new bloggers who publish quality content cannot rank higher on the SERP. For example, an IT expert tries to start a blog, but under the C-Rank algorithm, that blog cannot defeat other bloggers who’ve been creating IT-related content for a long time.
What’s more, Naver has put more value into content freshness, meaning that informative articles written a long time ago may not rank as high.
Naver Blog Search Algorithm: Deep Intent Analysis (June 2018-present)
Naver’s Deep Intent Analysis (DIA) algorithm puts more value into content that users prefer. Coupled with the C-Rank algorithm, the DIA algorithm ensures both the quality of content creators and the quality of the content itself by surfacing results that meet credibility scores and user preference.
What is the DIA algorithm and how does it work?
Under the Naver DIA algorithm, multiple factors, such as relevancy to the topic, user experience, content quality, uniqueness, and timeliness, work at once.
Put simply, content that is preferred by Naver users is considered to be of high quality and will therefore rank higher on the SERP (this works in quite a similar way to Google search).
Naver DIA algorithm (source: Naver Search Official Blog)
After Naver introduced the DIA algorithm, we have seen greater visibility and higher rankings of quality content, and informative reviews have also increased.
For example, before the DIA algorithm update, advertisements sometimes covered the blog SERP. After the DIA algorithm update, however, the blog SERP is pretty much advertisement-free and instead features informative content.
Before (left) and after (right) the Naver DIA algorithm update (source: Naver Search Official Blog)
Correlation between the Naver C-Rank and DIA Algorithms
These two algorithms are complementary to each other, making them effective in helping quality content rank higher on the Naver Blog SERP.
Based on the statistics of the DIA model, most bloggers with higher C-Ranks are generally writing content with higher DIA scores as well.
Naver C-Rank and DIA algorithm correlation
Naver Blog Search Algorithm: Similar Content Identification System (October 2018-present)
To protect copyrights, Naver has launched a system to identify plagiarized or similar content on the Naver Blog.
What is the similar content identification system and how does it?
The concept of the system is to display which piece of content is original, which is a pretty similar idea to the rel=canonical tag in Google.
Unfortunately, Naver doesn’t provide canonical implementation to their properties yet, so they have been strengthening the logic to protect original content from copied (or similar) content.
So, through the search option, users can choose whether to include copied versions or exclude them (as shown below).
Naver Blog Search: Include or exclude copied versions of content
If your content is original but classified as copied, you can ask Naver to double-check and reclassify.
Naver Blog Search Algorithm: Deep Intent Analysis Plus (Nov 2020-present)
What is the DIA+ algorithm?
As mentioned earlier, the DIA algorithm evaluates user-preferred content with a multi-factor credibility score and ranks them on Naver’s SERP.
However, search algorithms must be updated regularly to match user intent amidst ever-changing search environments.
Thus, the DIA+ algorithm was launched with several machine-learning improvements, including deep matching, search pattern analysis, and more dynamic rankings. Its underlying goal? Provide more accurate search results that match what users are searching for.
How does the DIA+ algorithm work?
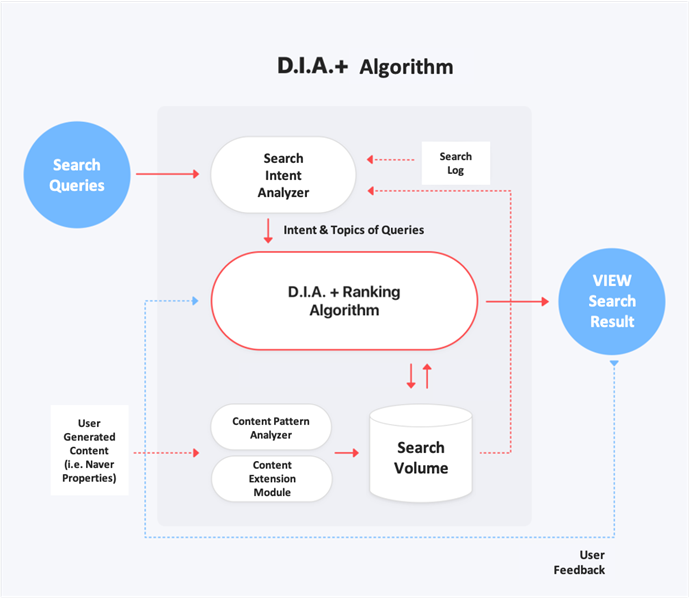
According to Naver, the DIA+ algorithm considers the following in its rankings:
Search Intent Analyzer
This considers patterns in user search queries based on cluster analysis.
Content Pattern Analyzer
This considers new patterns from the content’s structure, body text, and images.
Content Extension Module
This considers improving the quality of results by replacing meaningless words with meaningful ones recognized by the algorithm. Learn more about Naver’s Content Extension Module (auto-translate to English is recommended).
DIA+ Ranking
This considers diversifying results based on search pattern behaviors and user feedback.
User’s feedback
This considers user feedback to improve and update the search algorithm.
How Naver Blog search works under the DIA+ algorithm
What’s changed in the DIA+ algorithm?
Improved analysis of frequently searched queries
In the DIA+ algorithm, the enhanced analysis of user intent has helped produce better quality search results.
In other words, the algorithm analyzes search intent to determine how to best rank and tailor the comments and reviews in the VIEW search results for the user.
New featured snippets introduced on the SERP
The VIEW search analyzes and draws from thousands of user query patterns to create more personalized searches.
Following the update, the new featured snippets conveniently direct users to relevant information that answers their search query, drawing some similarities to Google’s featured snippets.
According to Naver, queries about pricing has accounted for approx. 20% of total search engine results. Examples of these include searches about flight ticketing information, phone repairs, and even expected monthly travel expenses.
So, let’s compare the featured snippets for these queries on Naver’s SERP versus Google’s.
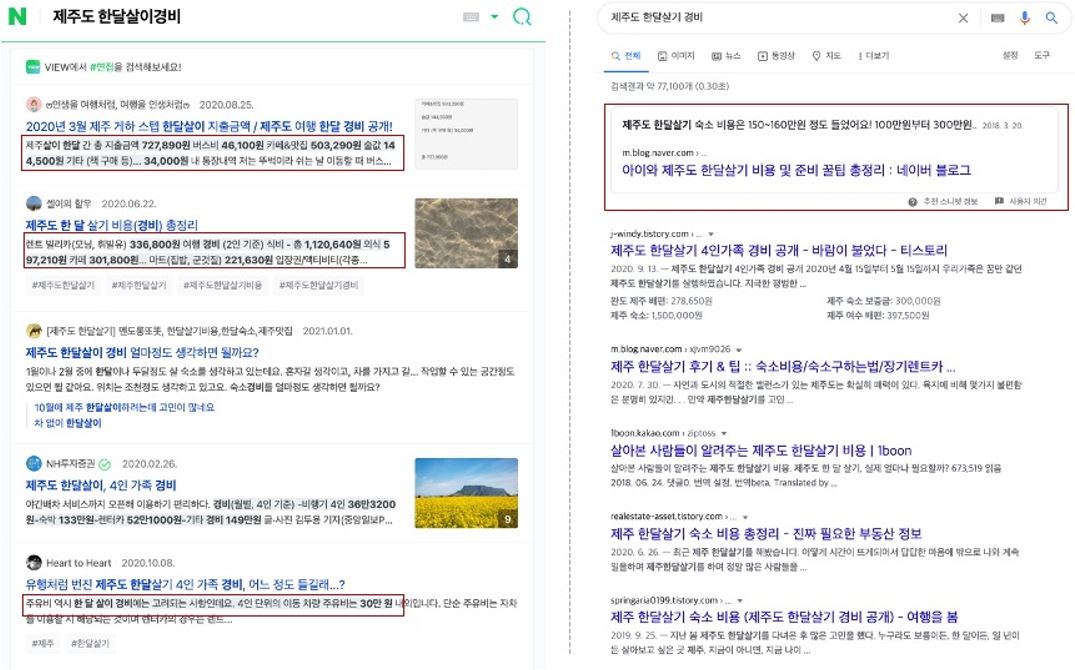
Naver’s featured snippets highlight (in grey) the most relevant information to a search query, while making them easily visible for users as they scroll down.
By contrast, Google’s featured snippet occupies a larger space atop the SERP, granting greater visibility than Naver’s.
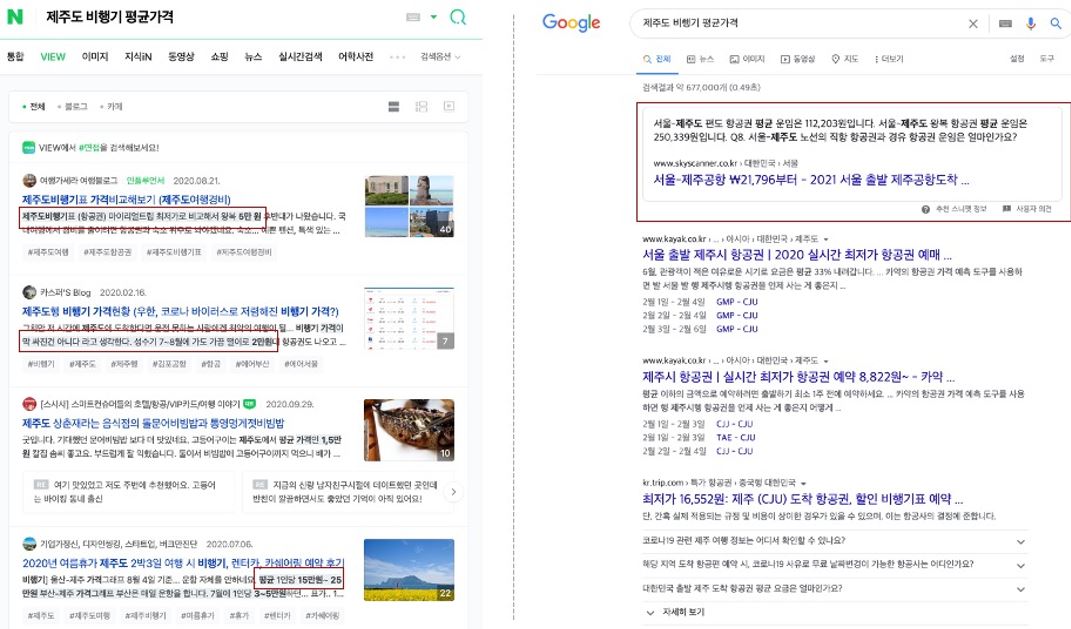
Among Naver’s properties, its VIEW section pushes more user-generated content (UGC). This means that results from official websites rarely, if ever, show up.
So, while search results of “flight tickets to Jeju Island” on Naver’s SERP are largely based on past user experiences, Google’s SERP showcases more travel websites. In the image above, for instance, Skyscanner is exhibited as a featured snippet on Google’s SERP.
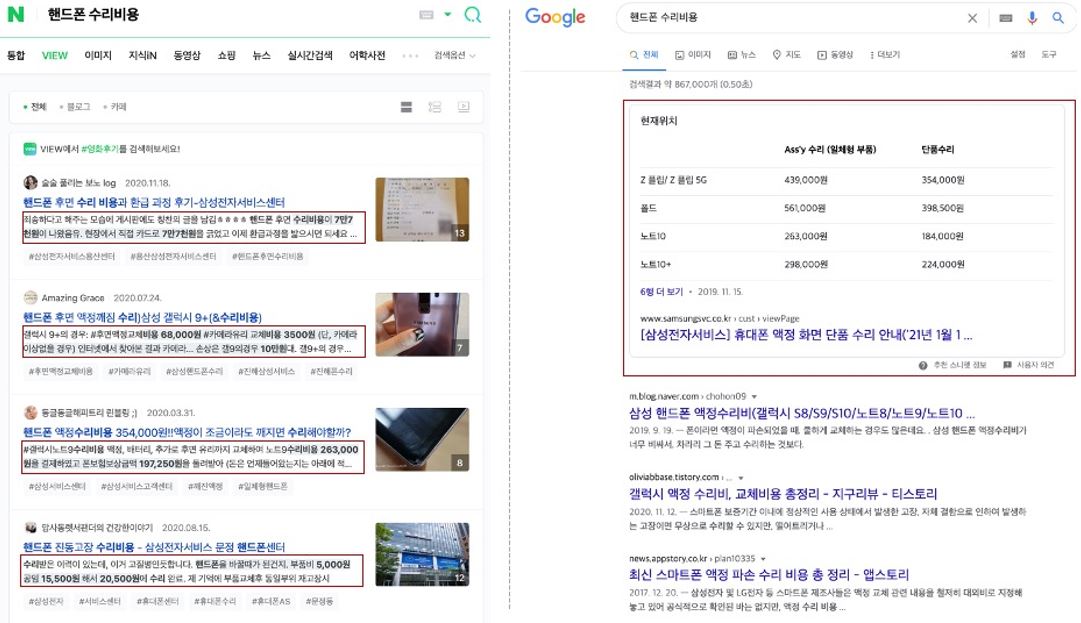
A quick search of “smartphone repair costs” on Naver will render experience-based results depending on the phone’s brand, model, and how long it’s been used.
Meanwhile, input the same search on Google, and Samsung’s official customer service webpage will show up as a featured snippet (Samsung dominates the South Korean smartphone market).
Thus, aside from the more recognized sources found on Google’s SERPs, chances are high that those seeking more personal search experiences would prefer the updated Naver VIEW search.
More sophisticated algorithm yields more relevant search results
Over the last couple of years, many Naver users have reported being shown content that doesn’t match their search intent. Indeed, Naver—particularly Naver Blog search—has been infamous for featuring phishing articles and low-quality content.
To rectify this, Naver has since updated its search algorithm with machine-learning capabilities to find content from more credible sources. To this end, we are seeing a rise in more accurate search results matching user intent with the DIA+ algorithm.
***
In the past, it was effective to create as many pieces of Naver-specific content as possible for SEO in Korea, whether that content was of high-quality or not. That’s why lots of black hat bloggers used irrelevant images and meaningless words over and over to increase the volume of their content.
For the last 2-3 years, however, how Naver’s Blog search works has changed. The C-Rank algorithm introduced in 2016 prioritizes content from professional creators, while the DIA algorithm ranks content based on user preference—and thus quality (very similar concept as the page ranking of Google). So, strategies that worked in the past (most likely black hat SEO) won’t work now.
Naver continuously evolves its blog search algorithm to understand users and their needs and provide the best quality content—and us bloggers should do the same!